IPv6 vs. IPv4: 7 Advantages and Disadvantages of IPv6 over IPv4
The move from IPv4 to IPv6 is a major update in how the internet functions. IPv6, or Internet Protocol version 6, was created to fix some of the limitations of IPv4, especially the limited number of IP addresses.
While IPv6 brings many improvements, it also has its own challenges. This guide breaks down the seven main advantages and disadvantages of IPv6 compared to IPv4 to help you understand the pros and cons of switching from IPv4 to this new internet protocol (IPv6).
Advantages of IPv6 Over IPv4
There had few drawbacks of IPv4 protocol which IPv6 protocol addressed to counter all drawbacks and enhance overall quality, stability and safety of modern networks. Following are few of the advantages of switching from IPv6 to IPv4:
- Expanded Address Space:
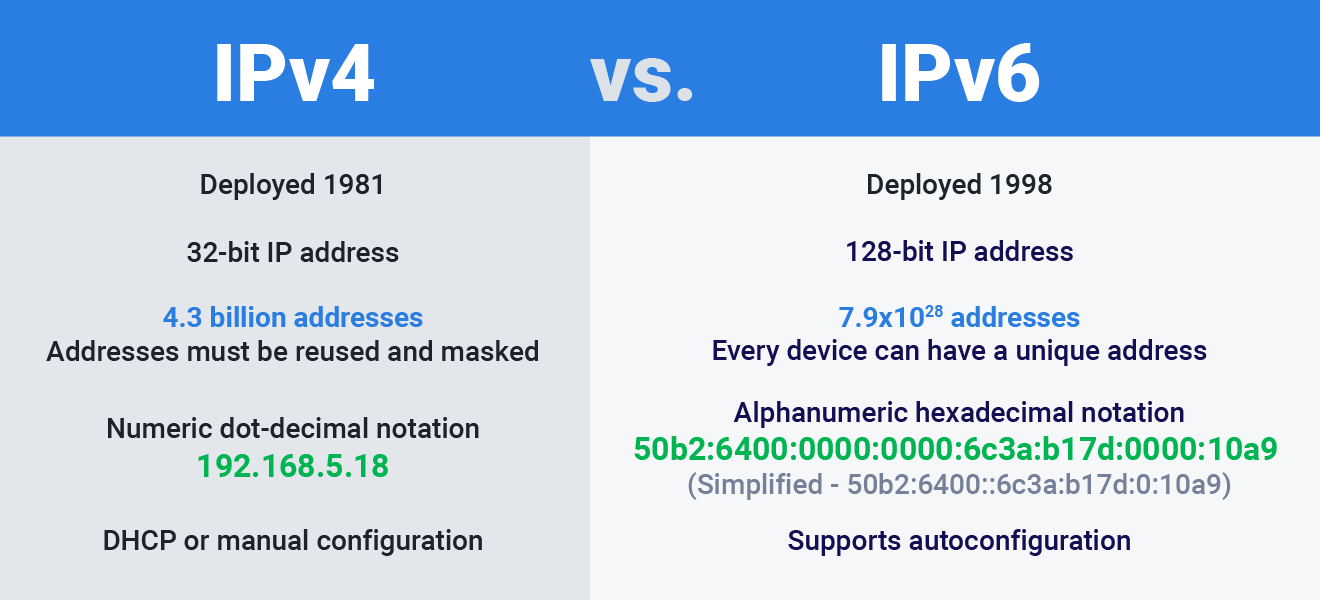
- IPv6 uses a 128-bit address system, which allows for around 340 undecillion (3.4 x 10^38) unique IP addresses.
- This large number of addresses solves IPv4’s issue of running out of IP addresses, making IPv6 capable of supporting the growing number of devices connected to the internet, from computers to smart home gadgets.
- Enhanced Security:
- IPv6 was designed with built-in security features.
- Unlike IPv4, which needs additional configurations for security, IPv6 includes IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) by default.
- This feature ensures data integrity, confidentiality, and verification of the data’s origin, offering stronger protection for online communication.
- Better Routing and Faster Network Performance:
- IPv6 makes routing more efficient by simplifying packet headers (the information in each data packet).
- This simplification allows routers to process data more quickly, improving overall network speed.
- IPv6 also has a structured address format that reduces the size of routing tables, which leads to faster and more optimized routing.
- Improved Multicasting:
- IPv6 has better support for multicasting, which allows one data packet to be sent to multiple destinations at once.
- This feature is particularly helpful for applications like video streaming, online gaming, and video calls, as it reduces bandwidth usage and improves performance for data-heavy applications.
- Automatic Configuration:
- IPv6 supports automatic address configuration through a process called Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC).
- This feature enables devices to automatically set up their IP addresses without manual input, making it easier to deploy large networks, especially for IoT (Internet of Things) devices.
- Simplified Network Management:
- With IPv6, devices can automatically update their IP addresses when network changes occur, reducing the need for DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) servers.
- This capability simplifies network management and makes it easier to maintain large, dynamic networks.
- No Need for Network Address Translation (NAT):
- IPv4 often requires NAT (Network Address Translation), which allows multiple devices to share a single public IP address.
- However, NAT can slow down performance and cause compatibility issues.
- IPv6’s large address space removes the need for NAT, allowing direct device-to-device communication for better reliability and speed.
Disadvantages of IPv6 Over IPv4
IPv6 comes with many advantages for sure, but along with advantages, it comes with fair share of disadvantages, or we can call it challenges. Following is few of the disadvantages/challenges of IPv6 compared to IPv4:
- Compatibility Issues with IPv4:
- IPv6 and IPv4 are not directly compatible, which means additional measures are needed for them to work together.
- Many organizations need to use dual-stack systems (supporting both IPv4 and IPv6) or tunneling to allow communication between the two.
- These methods can add complexity and cost, slowing down IPv6 adoption.
- Limited Support in Older Devices:
- More Complex Network Management:
- IPv6 addresses are 128 bits long, compared to IPv4’s 32-bit addresses, making them harder to remember and manage manually.
- The hexadecimal format of IPv6 addresses can be confusing, increasing the chances of mistakes and making network management more challenging.
- Security Concerns During the Transition Phase:
- Higher Implementation Costs:
- Slow Adoption and Limited ISP Support:
- Although IPv6 was introduced over a decade ago, adoption has been slow, especially among ISPs (Internet Service Providers) in some areas.
- If ISPs don’t offer IPv6, companies and individuals may have to keep using IPv4, slowing down the full transition to IPv6.
- Complexity:
Conclusion
IPv6 is a necessary upgrade for a growing, secure internet, offering a larger address space, improved security, and easier network management.
However, IPv6 also brings challenges, such as compatibility issues, costs, and added complexity, that must be considered. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of IPv6 over IPv4 helps organizations make informed choices about when and how to transition to this new protocol.
Read more about Advantages of IPv4 Protocol in the linked article.