What is IPsec? Advantages, Limitations, Applications, Components and Modes
In today’s interconnected world, securing data during its transfer over the internet is more critical than ever. One of the most powerful protocols designed to ensure secure communication is IPsec (Internet Protocol Security). Widely used in VPNs, IPsec plays a crucial role in protecting sensitive data as it travels over potentially unsecured networks. This article provides an in-depth look at IPsec, its working principles, components, and its applications in today’s network environments.
What is IPsec?
IPsec, or Internet Protocol Security, is a suite of protocols designed to secure internet communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet in a data stream. It operates on the network layer (Layer 3 of the OSI model), making it versatile and widely applicable across different networks. IPsec is used for establishing VPNs (Virtual Private Networks), securing data between two devices or networks, and enhancing privacy and integrity in IP communication.
Key Benefits of IPsec
- Data Confidentiality: Encrypts data to prevent unauthorized access.
- Data Integrity: Ensures data is not altered during transmission.
- Authentication: Verifies the identity of the communicating parties.
- Anti-Replay: Prevents hackers from intercepting and re-sending packets to gain unauthorized access.
How Does IPsec Work?
IPsec secures data in three main ways: Encryption, Authentication, and Data Integrity. The combination of these elements enables IPsec to protect IP packets and prevent unauthorized access or tampering.
1. Encryption
- IPsec uses encryption to scramble data, making it unreadable to anyone without the appropriate decryption key. Popular encryption algorithms for IPsec include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and 3DES (Triple Data Encryption Standard).
2. Authentication
- Authentication in IPsec verifies that data is being sent and received by authorized users. IPsec utilizes digital certificates and pre-shared keys (PSKs) to establish and verify the identities of both ends of the connection.
3. Data Integrity
- Data integrity checks ensure that no unauthorized modifications are made to the data during transmission. IPsec employs hash functions, such as SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm), to detect any tampering.
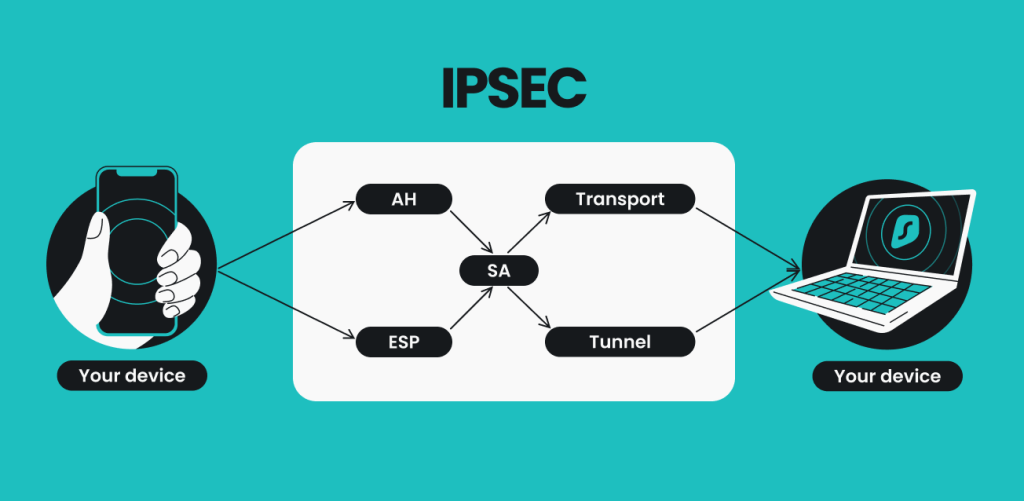
Key Components of IPsec
IPsec relies on several core components to function effectively, including AH (Authentication Header), ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload), and IKE (Internet Key Exchange).
1. Authentication Header (AH)
- The Authentication Header is responsible for authenticating the IP packet’s sender. AH provides data integrity and anti-replay protection but does not encrypt the data, meaning the content of the packet is still visible.
2. Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
- ESP is used to both authenticate and encrypt IP packets. Unlike AH, ESP provides data confidentiality in addition to integrity and anti-replay protection, making it more commonly used in applications requiring high security.
3. Internet Key Exchange (IKE)
- IKE is a protocol used to set up a secure connection between devices. It establishes a security association (SA), which defines the encryption and authentication methods used in the IPsec connection. IKE uses Diffie-Hellman key exchange to create shared encryption keys.
IPsec Modes of Operation
IPsec can operate in two primary modes: Transport Mode and Tunnel Mode. Each mode serves different use cases and security needs.
1. Transport Mode
- In Transport Mode, IPsec only encrypts the data portion (payload) of each packet, leaving the IP header unchanged. This mode is often used for end-to-end communications, such as between two devices on a private network. Transport Mode is commonly deployed in internal networks where the IP address doesn’t need to be hidden.
2. Tunnel Mode
- Tunnel Mode encrypts the entire IP packet, including the header and payload. It is often used in VPNs, where data must pass through public networks. Tunnel Mode encapsulates the original IP packet within a new IP packet with a new header, effectively hiding the sender’s IP address for added security.
Applications of IPsec
IPsec’s robust security features make it popular in a range of applications, especially in environments requiring secure remote access, private networks, and data confidentiality.
1. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
- IPsec is widely used in VPNs to secure data transmitted over the internet. By creating a secure “tunnel” between devices, IPsec VPNs enable remote users to access corporate networks safely. Many organizations use IPsec VPNs to allow employees to work remotely while keeping sensitive data secure.
2. Secure Remote Access
- With the rise of remote work, IPsec is commonly used to provide secure access to corporate resources. IPsec enables encrypted communication between employees’ devices and the organization’s network, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality.
3. Site-to-Site Connections
- IPsec is used to create secure connections between different sites or branch offices of an organization. By securing data exchanges between sites, IPsec helps maintain data privacy and prevents unauthorized access across distributed networks.
4. E-commerce and Online Banking
- IPsec plays a role in securing online transactions, providing encryption and authentication for financial data exchanges in e-commerce and online banking applications.
Advantages of IPsec
- Robust Security: Provides end-to-end encryption, authentication, and data integrity.
- Scalability: Operates on the network layer, allowing it to secure data across various types of networks.
- Privacy and Confidentiality: Ensures sensitive data remains private during transmission.
- Widely Supported: IPsec is compatible with major VPN technologies and widely supported across devices and platforms.
Limitations of IPsec
- Complex Configuration: IPsec requires careful setup and management, which can be complex and time-consuming.
- Performance Overhead: Encryption and decryption processes may impact network performance, especially in high-traffic environments.
- Limited Compatibility: While IPsec is widely used, some network environments or legacy devices may not support it fully.
- Higher Cost: Implementing IPsec may involve additional costs, especially if upgrading hardware and training staff is required.
Conclusion
IPsec remains a foundational protocol for securing data over the internet. Its encryption, authentication, and data integrity features make it essential for VPNs, secure remote access, and site-to-site connections. Despite some limitations, IPsec’s benefits far outweigh its drawbacks in applications where data security and privacy are paramount. By understanding IPsec’s functions and applications, organizations can better protect their sensitive information and establish secure, reliable network connections.